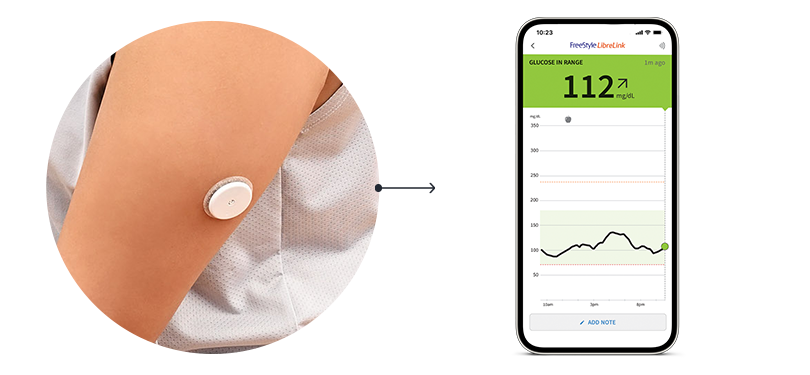
This is progress.
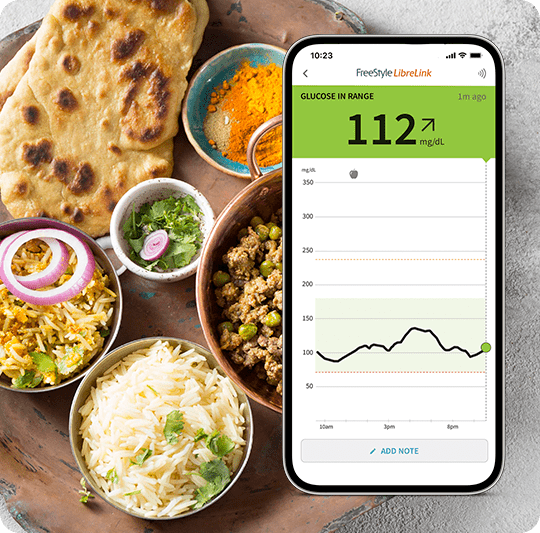
Daily glucose spike at lunchtime.
See a pattern here?
Wonder why your glucose dips at a certain time of day? Or what foods cause a spike? FreeStyle Libre CGMs show you how meals, workouts, and medication can impact your glucose. These unique patterns can help identify what you’re doing right and areas you can improve upon.
Learn from others who have been there.
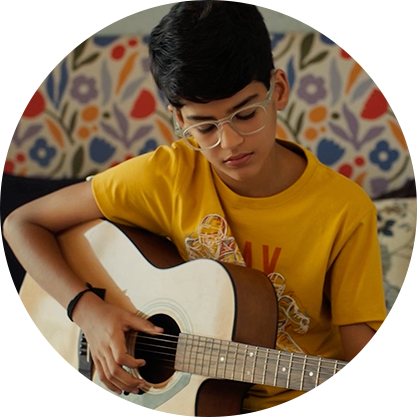

"Earlier, I didn't have the energy to walk up a flight of stairs. With FreeStyle Libre, I can track and share my glucose levels, avoid low glucose and manage my energy levels. The best part is that my parents worry less."
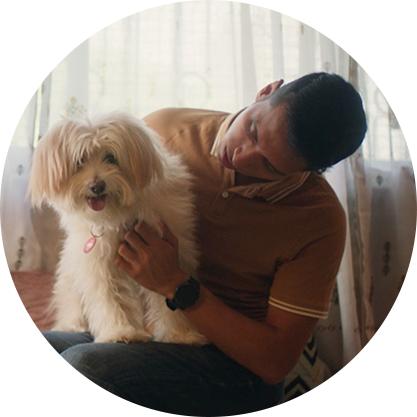

"With Freestyle Libre, I can now monitor my glucose levels even in school to help me predict hypoglycemic events and share the readings with my parents. This allows me to play all the games I love without having to worry anymore."

Diabetes is a
balancing act.
We can help.
Are you currently using FreeStyle Libre or starting your first sensor and looking to learn more about managing your glucose and diabetes? Sign up for the MyFreeStyle program and get helpful insights on how food and exercise affect glucose levels, advice for tracking your progress, and much more.

ADC-116458 v2.0