Hypoglycemia can228:
- Provoke tense-tiredness (a feeling of being both tense and tired at the same time) and feelings of unhappiness
- Increase irritability and anger
- Make us pessimistic about everyday situations and about life issues
- Lead to mood changes, which are negative, stressful and unpleasant
- Lead to anxiety (with repeated episodes of hypoglycemia)
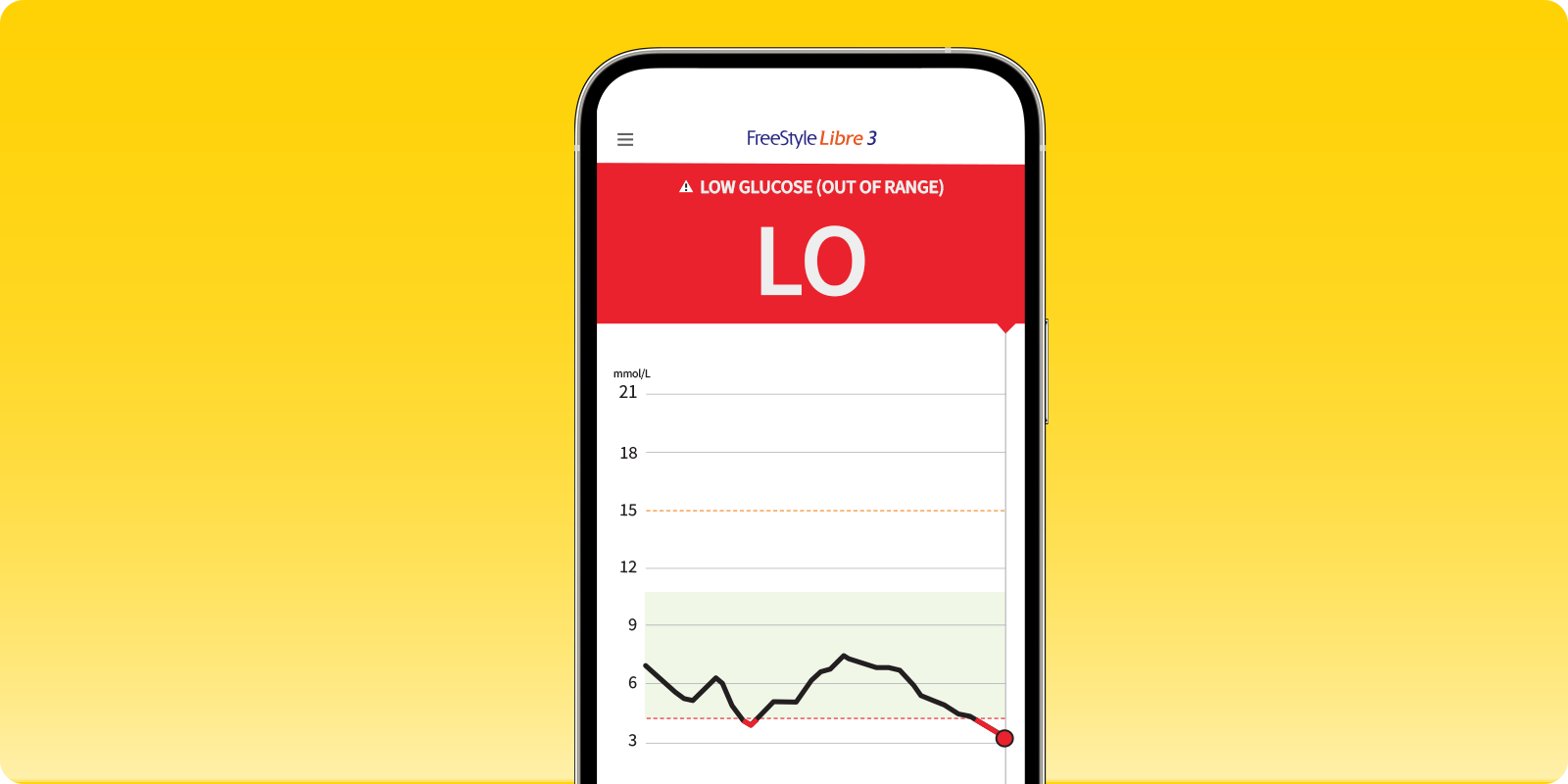
Hypoglycemia can also cause cognitive (mental) impairment. Studies have shown that mental function can be affected when glucose levels fall below 3.0 mmol/L. Below this level, people with diabetes may start to experience problems with225:
- Fine motor coordination
- Mental speed
- Concentration
- Certain memory functions (e.g., word recall, working memory)
Finally, hypoglycemia can cause some uncommon but serious consequences to other parts of the body including the brain (coma, seizures, mental impairment, psychological effects225), bones (falls, accidents, dislocations, driving mishaps225), and the heart (angina or chest pains, abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure225,229).





Stay Connected